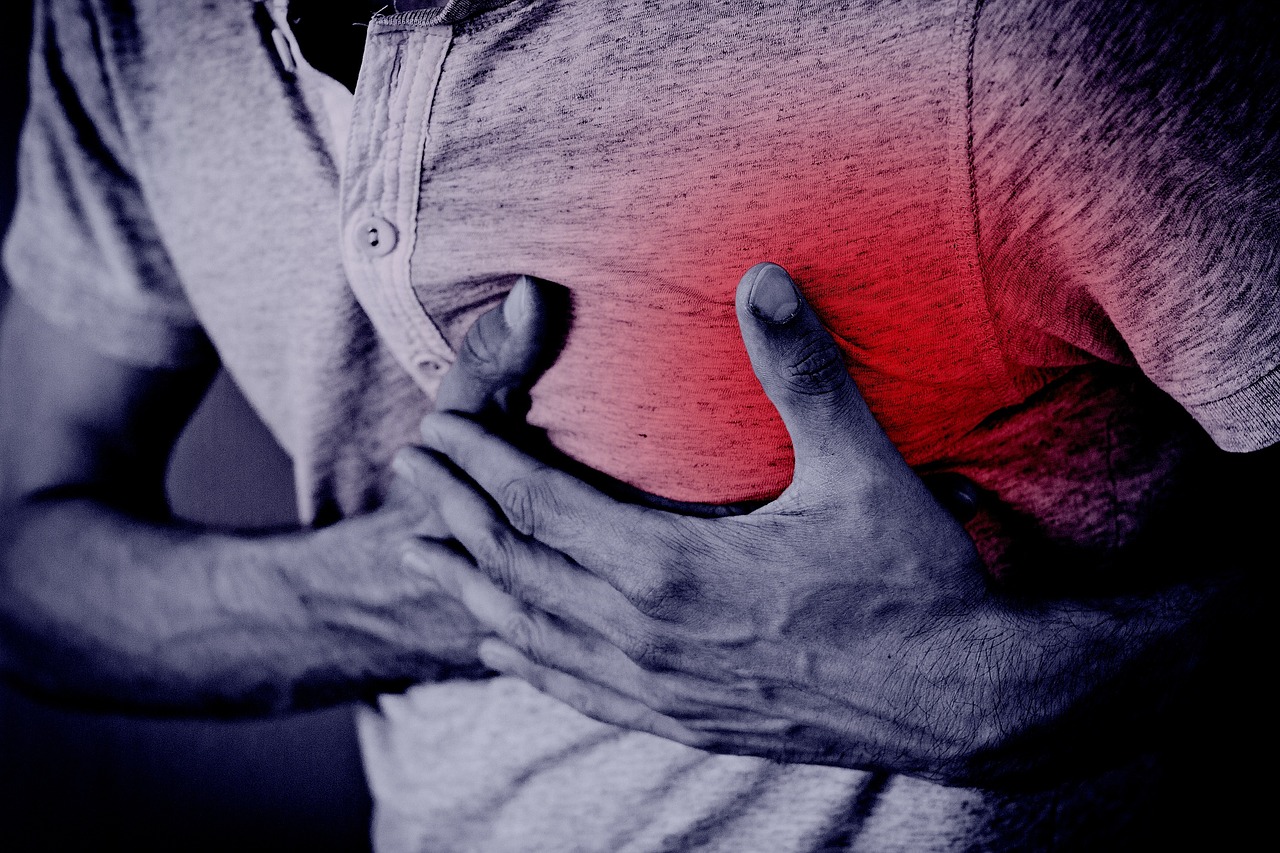
Diabetes and heart disease are closely connected, with individuals diagnosed with diabetes being at a significantly higher risk of developing cardiovascular complications. High blood sugar levels, insulin resistance, and inflammation contribute to arterial damage, increasing the likelihood of heart attacks, strokes, and other heart-related issues. Understanding this link is essential for managing risk and taking proactive steps toward better health.
How Diabetes Affects the Heart
Diabetes impacts heart health in several ways, primarily through the following mechanisms:
1. High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia) and Arterial Damage
Excess glucose in the bloodstream can cause damage to blood vessel walls, making them stiff and prone to plaque buildup. Over time, this leads to atherosclerosis, a condition where arteries narrow and restrict blood flow, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
2. Insulin Resistance and High Blood Pressure
Many people with type 2 diabetes experience insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells don’t respond properly to insulin. This can lead to hypertension (high blood pressure), which puts additional strain on the heart and arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
3. Chronic Inflammation and Increased Cholesterol
Diabetes often leads to chronic inflammation, which contributes to the development of fatty deposits in blood vessels. Additionally, people with diabetes tend to have abnormal cholesterol levels—higher levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) and lower levels of HDL (good cholesterol). This imbalance further raises the risk of cardiovascular disease.
4. Obesity and Heart Disease Risk
Obesity is a common factor in type 2 diabetes and is strongly linked to heart disease. Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, contributes to insulin resistance, increased cholesterol levels, and higher blood pressure—all of which increase cardiovascular risk.
Warning Signs of Heart Disease in Diabetics
People with diabetes should be aware of early warning signs of heart disease, which may include:
Chest pain or discomfort
Shortness of breath
Fatigue or weakness
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Swelling in the feet, ankles, or legs
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately, as they could indicate a heart-related issue.
How to Reduce Heart Disease Risk with Diabetes
While diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, lifestyle changes can help reduce the chances of developing cardiovascular complications.
1. Maintain a Heart-Healthy Diet
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods rich in fiber, lean protein, and healthy fats.
Avoid refined sugars, trans fats, and excessive sodium.
Incorporate foods like leafy greens, fatty fish, whole grains, and berries to support heart health.
2. Stay Physically Active
Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Include a mix of aerobic activities (walking, cycling) and strength training.
Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular function.
3. Manage Stress Levels
Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga.
Get enough sleep to support overall well-being.
Reduce chronic stress to prevent spikes in blood sugar and blood pressure.
4. Monitor Blood Sugar, Blood Pressure, and Cholesterol
Keep blood sugar levels in check through proper diet and medication if needed.
Regularly check blood pressure to ensure it stays within a healthy range.
Monitor cholesterol levels and take action if needed to balance LDL and HDL.
5. Consider Natural Supplements for Heart and Blood Sugar Support
Certain supplements may help reduce inflammation, support blood sugar control, and promote heart health:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids – Helps reduce triglycerides and inflammation.
Magnesium – Supports blood pressure and glucose metabolism.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) – Promotes heart function and energy production.
Berberine – A natural compound that helps regulate blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the connection between diabetes and heart disease is crucial for taking proactive steps toward better health. By managing blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and monitoring key health markers, you can significantly reduce your risk of cardiovascular complications.
Looking for natural supplements to support heart and blood sugar health? Visit CardioForte4Life.com for high-quality products designed to keep you healthy!
Remember, you don’t need to overhaul your diet overnight. Start with small, manageable changes—like swapping white bread for whole grain or adding an extra serving of veggies to your dinner plate.
Complement your heart-healthy diet with supplements like CardioForLife Powder to fill in any nutritional gaps and support overall cardiovascular health.